Perspective correction with Python (openCV)
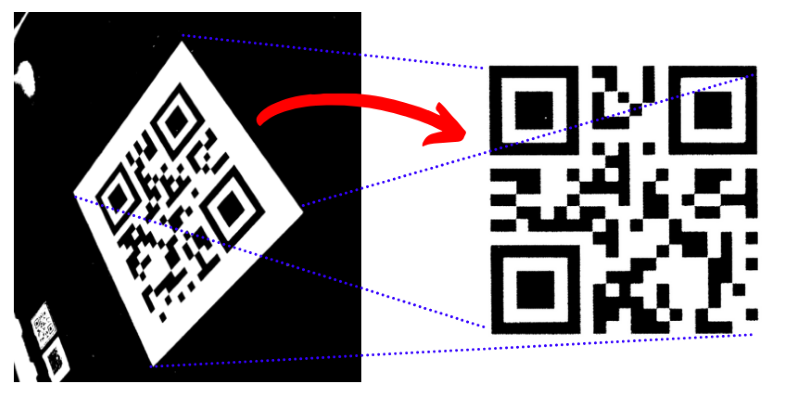
A practical guide of perspective correction, with a typical use case: correct the orientation of a QR code. This can be used as a pre-processing step before applying your algorithms to decode the QR code.
Check HERE how to decode a simple QR code
The job is to apply a transformation matrix on our original image in order to correct to perspective of the picture and to end up with a flat and aligh QR code.
OpenCV provide a function to compute such a transormation matrix by giving it 4x input points and providing the 4x target output points.
Illustratively, what we would like to achieve is the following:
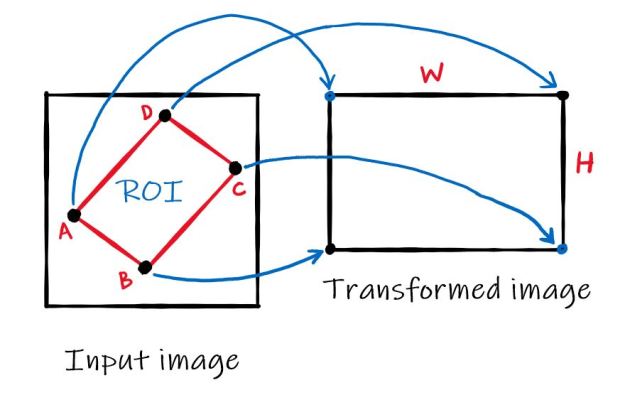
(Source: theailearner)
What is needed is to correctly find those 4x input points, which should correspond to our original QR code corner.
Load original QR code
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (10,10)
# open your QR image
img = cv2.imread("samples/QR_warp.jpg", cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # open in grayscale
#img = cv2.imread("samples/QR_warp_2.jpg", cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # open in grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) #convert to gray
plt.imshow(img)
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1f10c59ba00>
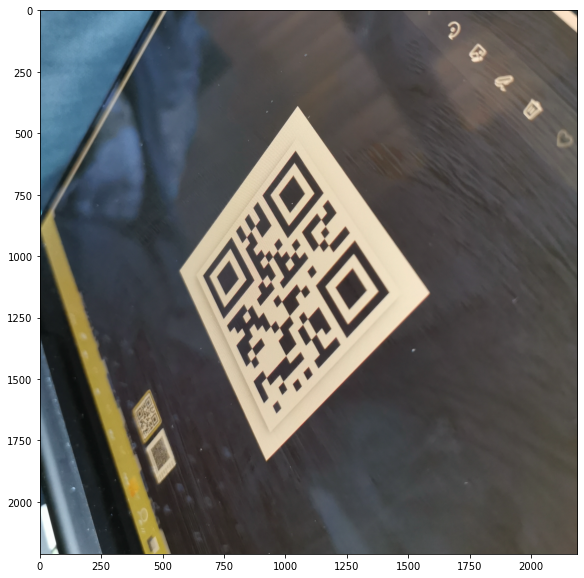

This QR code is currently not readable as is.
Pre-processing
Threshold the image to deal with black and white pixels only
# thresholding, all pixel > 120 will be set to 255, the other to 0
_, gray = cv2.threshold(gray, 120, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
plt.imshow(gray, cmap='gray')
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1f10f1ff850>
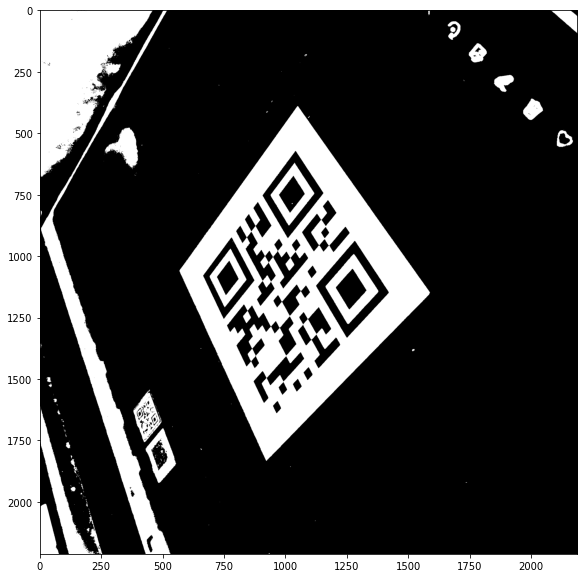

Edge detection
Perform edge detection algorithms. This will greatly help for further contour detections
# edge detection
edges = cv2.Canny(gray,50,110)
# dilatation to make and merge the lines
dil_kernel = np.ones((5,5), np.uint8)
edges=cv2.dilate(edges,dil_kernel,iterations=1)
plt.imshow(edges, cmap='gray')
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1f10f179f70>

Contour and find the original corners
The first step is to compute the contours in the ‘edges’ picture. The biggest contour is most probably the bounding box of the QR code.
From there, we have to find the 4 corners of the QR code, and this is achieve with the function approxPolyDP()
# find all countour
cnts, hierarchies = cv2.findContours(edges, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# biggest countour is most probably our ROI (Region of interest)
big_idx = 0
biggest_area = 0
for i in range(len(cnts)):
cnt = cnts[i]
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
if(area > biggest_area):
biggest_area = area
big_idx = i
# draw this contour
cnt = cnts[big_idx]
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (255,0,0), 5)
# find the contour approximation
epsilon = 0.06*cv2.arcLength(cnt, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt, epsilon, True)
assert len(approx) == 4
corners = np.empty((0, 2), np.float32)
for p in approx:
corners = np.append(corners, np.array([p[0]]), axis=0)
cv2.circle(img ,tuple(p[0]),10,(0,255,0), 10)
print("Corners data points: {}".format(corners))
plt.imshow(img)
Corners data points: [[1050. 388.]
[ 565. 1055.]
[ 917. 1834.]
[1587. 1151.]]
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1f10f3d8ac0>
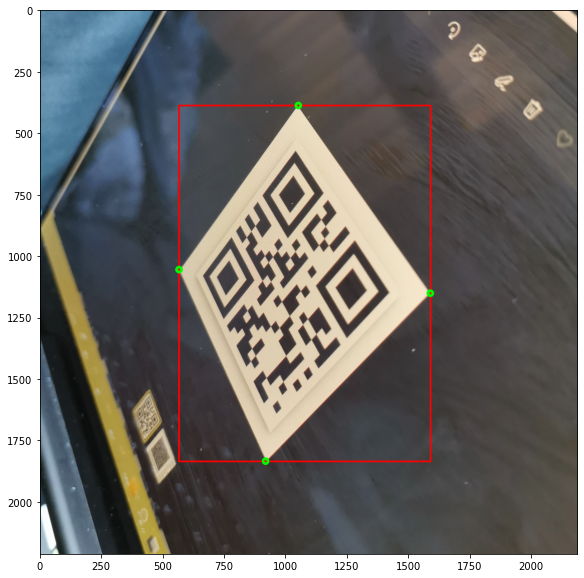

Make the transformation
Once we have the original 4x corners, the job is done. We only have to apply a couple of image processing functions to compute the matrix and to apply the transformation matrix to our original image.
# compute the perspective transformation matrix
out_size = 500 # 500x500
in_pts = np.array(corners, np.float32)
out_pts = np.array([[0, 0],
[0, out_size],
[out_size, out_size],
[out_size, 0]], np.float32)
M_transform = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(in_pts,out_pts)
# make the transformation (on gray img)
out = cv2.warpPerspective(gray, M_transform,(out_size, out_size),flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
plt.imshow(out, cmap='gray')
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x1f10f443970>
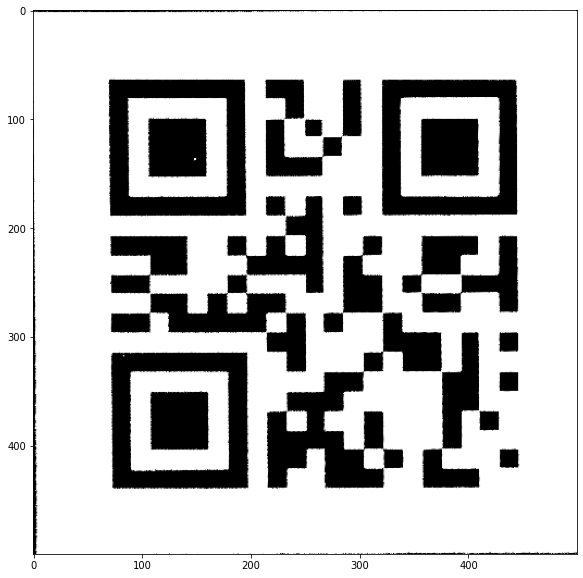

The end result is pretty satisfying. The above output image can now be decoded.
If you now want to decode it, you can Check HERE how to decode a simple QR code.